
The development of the circular economy model is regarded as an inevitable recently, in line with the trend and requirements for achieving a breakthrough in economic recovery and implementing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), thereby contributing to the realization of the national strategy for green growth.
- Circular economy – The foundation for Vietnam’s sustainable development
- Development and sustainable development: What is the difference?
- The transportation sector shifts to renewable energy and reduces greenhouse gas emissions
What is the circular economy
Since 1990, David W. Pearce and R. Kerry Turner have used the term circular economy in The Economics of Natural Resources and Environment. In contrast to the old linear economy, the term refers to a new economic model based on the basic principle that “everything is an input to everything else.”
Many parties then proposed the concept of the circular economy since the approach from research and application perspectives is unique. For example, according to the European Union (EU) “The circular economy is a model of production and consumption, which involves sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing and recycling existing materials and products as long as possible. In this way, the life cycle of products is extended.” Meanwhile, the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO) defines the term as a closed production cycle in which wastes are returned as raw materials for manufacturing, therefore decreasing any negative impacts on the environment, ecosystems, and human health.
A concept introduced in 2012 by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation has generally been accepted more by many nations and international organizations. Accordingly, “the circular economy is a restore and renewable system achieved by proactive planning and design. It replaces the concept of “end of life cycle” of materials with the concept of restoration, shifting toward the use of renewable energy, refraining from using harmful chemicals that harm reuse, and aiming to reduce waste through the design of materials and products, technical systems, and business models within the scope of that system.”
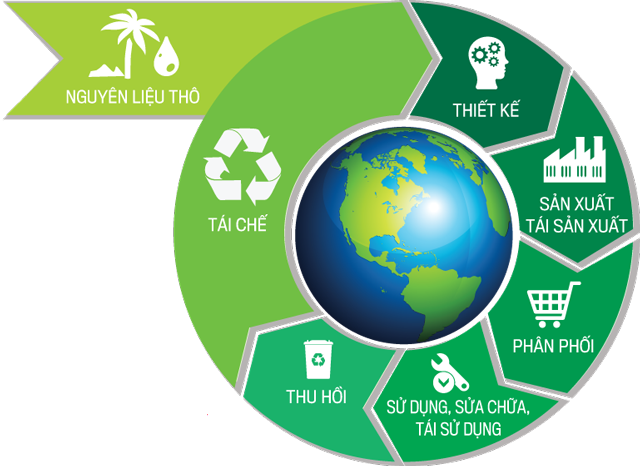 Circular economy model
Circular economy model
Principles and some circular economy models
According to the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, there are three principles of the circular economy: Design out waste and pollution; Keep products and materials in use; Regenerate natural systems.
General provisions for the circular economy are listed in Article 138 of Decree No. 08/2022/ND-CP, which details many provisions of the Law on Environmental Protection:
– Reduce the exploitation and use of non-renewable resources and water resources; increase efficiency in the use of resources, raw materials and materials; save energy;
– Extend the useful life of materials, equipment, products, goods, and components;
– Restrict waste generated and minimize adverse impacts on the environment including reducing solid waste, wastewater and emissions; reducing the use of toxic chemicals; recycling waste, recovering energy; reducing disposable products; develop green purchasing habits.
There are now some circular economy models in use, such as the 3R model with a simple approach or the 6R+ model with a more comprehensive approach. The 3R model focuses on three activities: Reduce – Reducing the use of goods and resource consumption, Reuse – Reusing products and resources, and Recycle – Recycling and recirculating resources.
 Circular economy model with 3R: Reduce, Reuse and Recycle
Circular economy model with 3R: Reduce, Reuse and Recycle
Meanwhile, the 6R+ model includes:
– Rethink and Redesign: When producing any new product, manufacturers change their thinking and approach regarding responsibility for recovery, reuse, and recycling… while also improving and changing the design of products and commodities in production.
– Refuse: Consumers support green products, refuse to purchase environmentally unfriendly, resource-intensive goods, energy in the manufacturing/usage process, are not recyclable…
– Reduce: Reduce excessive consumption that leads to attrition and exhaustion of natural resources through shared, shared, and stored models…
– Reuse: Instead of just utilizing the product once, utilize it several times
– Remain và Repair: The manufacturer assures the formation and supply of services on warranty, maintenance, component replacement, repair… to prolong the life and life cycle of the product.
– Recycle: Resource recovery includes collection, sorting, garbage disposal, and recycling…
Circular economy model – A inevitable trend
The linear economic development model is no longer suitable in the context of more exhausted resources, fast industrialization and urbanization leading to increased greenhouse gas emissions, environmental quality decrease, and climate change bringing increasingly significant effects. The circular economy has emerged as a necessity and an inevitable trend. Developing a circular economy model is crucial because it promotes sustainable growth while also contributing to achieving emission reduction and carbon neutrality commitments, providing many benefits to the nation and enterprises.
Since the 1980s, Vietnam has had some circular economy models, including the garden-pond-barn (VAC) model. It is nearly a circular economy model in agriculture, but incomplete and mostly utilized on a small scale. It also first showed the efficiency and benefits of the circular economy. Many initiatives for sustainable corporate governance and the promotion of the circular economy have been proposed and progressively implemented in recent years. More and more businesses are paying attention and investing in improvements to gradually develop the circular economy model, implementing green production solutions such as using sustainable raw materials, utilizing clean energy, practicing energy conservation, and constructing collection and recycling processes…
 Many businesses use clean energy to green manufacture, toward a circular economy model and sustainable development
Many businesses use clean energy to green manufacture, toward a circular economy model and sustainable development
In June 2022, the Prime Minister released Decision No. 687/QD-TTg authorizing Vietnam’s Circular Economy Development Project. Some of the particular goals in this Decision:
- Contribute to the realization of the goal of reducing GHG emission intensity to GDP by at least 15% by 2030 compared to 2014, with the ultimate aim of achieving net zero emissions by 2025.
- Circular economy projects will begin to be implemented by 2025, promoting economic, social, technical, and environmental efficiency; reducing energy consumption and increasing the amount of renewable energy in the total primary energy supply…
- By 2030, circular economy projects will be a major driver in reducing primary energy consumption, with the ability to regulate most or all of the energy demands using renewable energy…
- By 2025, 85% of plastic garbage generated will be reused, recycled, or treated; 50% of plastic waste in the seas and oceans will be reduced…
- By 2030, the proportion of municipal solid waste collected and processed to fulfill standards and regulations through circular economy models will reach 50%; 100% of organic waste in urban areas and 70% in rural areas will be recycled..
The full text of Decision No. 687/QD-TTg authorizing the Circular Economy Development Project in Vietnam (released on 07/6/2022) may be found here.
Vu Phong Energy Group









