
At the COP26 conference, over 100 nations committed to reducing emissions including Carbon neutral, achieving a net emissions level of zero, and reducing methane gas emissions… Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and developing low-carbon economies to achieve Net Zero emissions have become the mainstream global development journey. To learn more about this trend, Vu Phong Energy Group invites you to explore some related terms!
Vietnam’s commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions
Leaders from over 100 participating nations responded in the fight against climate change at the 26th Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (COP26) in November 2021, and several important agreements were reached. These included targets to reduce methane gas emissions, achieve carbon neutrality, and achieve Net Zero Emissions. At the time, the Head of the Vietnamese delegation to the conference, Prime Minister Chinh, Pham Minh, also emphasized Vietnam’s commitment, stating that “Vietnam will build and implement strong measures to reduce greenhouse gas emissions using its resources, along with the cooperation and support of the international community, both in terms of finance and technology transfer, including implementing mechanisms under the Paris Agreement, to achieve a net emissions level of ‘0’ by 2050.“
What is Net Zero, carbon neutral (or carbon neutrality)?
The objective of obtaining Net Zero Emissions is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to near zero, with any emissions that remain being absorbed from the atmosphere by forests and oceans. This objective strives to mitigate the worst effects of climate change while preserving a livable planet. According to calculations, global temperature rise should be limited to no more than 1.5°C over pre-industrial levels. To do this, the world must reduce emissions by 45% by 2030 and reach net zero by 2050.
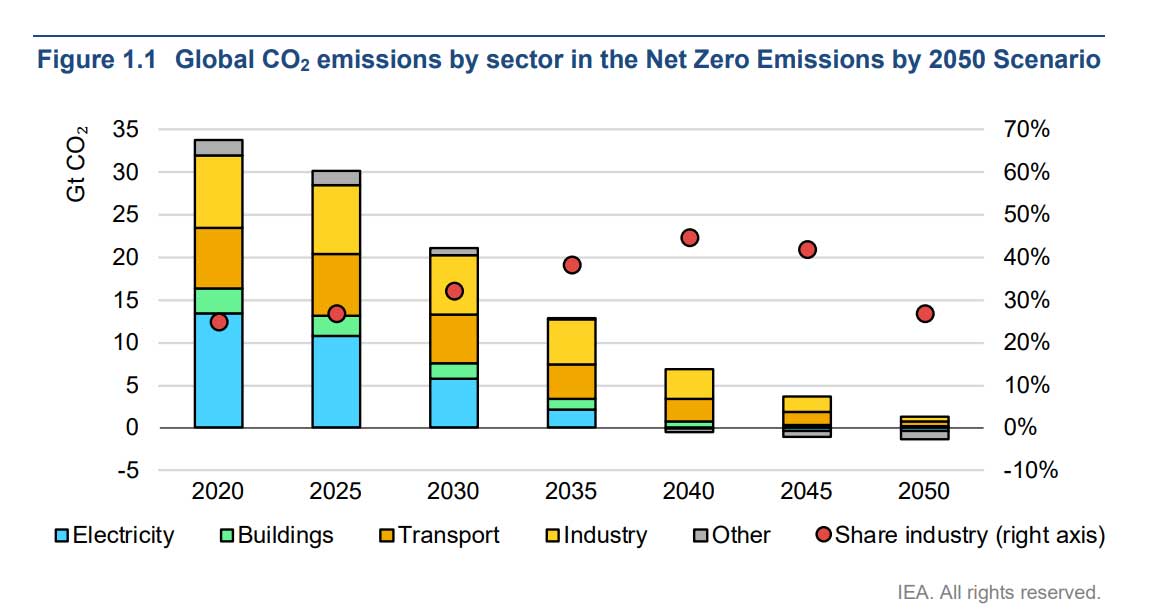 Global CO2 emissions by sector in the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario, IEA source
Global CO2 emissions by sector in the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 Scenario, IEA source
The Kyoto Protocol defines greenhouse gas emissions as CO2, CH4, N2O, HFCs, PFCs, and SF6. The quantity of greenhouse gas emissions is transformed into carbon emissions, and data is collected nationwide. According to the updated Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC) report for 2022, Vietnam has voluntarily increased its commitment to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 15.8% by 2030 compared to the Business-As-Usual (BAU) scenario, which is equivalent to 146.3 million tons of CO2 (compared to 9% in the NDC 2020 report). With international support, the reduction rate will rise to 43.5%, equal to 403.7 million tons of CO2 (up from 27% in the NDC 2020 report).
In addition to the goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and carbon emissions, other terms such as carbon neutral and climate neutral are also used.
What is the meaning of the term “Carbon footprint”?
The term “carbon footprint” refers to the entire amount of CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions (typically measured in tons of CO2 equivalent) generated by a product, person, or organization… A person’s carbon footprint comprises the total amount of emissions from everyday activities such as energy usage, food consumption, and consumer goods use… The carbon footprint of a product is determined as the total quantity of greenhouse gas emissions from raw materials, manufacture, transportation, consumption, and disposal… Carbon footprinting on a larger scale, such as a business, entails accounting for greenhouse gas emissions, identifying and quantifying the main sources of emissions, such as direct emissions from activities, emissions from purchased electricity and heat, and other indirect emissions not owned or directly controlled by the entity.
In the context of sustainable development, businesses often strive to reduce their carbon footprint by implementing emission reduction measures such as improving energy efficiency, switching to clean and renewable energy sources, using environmentally friendly materials, avoiding single-use products, and promoting reuse and recycling.
 Use renewable energy – an effective way to reduce emissions for the factory
Use renewable energy – an effective way to reduce emissions for the factory
What is carbon offset?
Carbon offset, also known as carbon compensation, is one of the efforts to reduce emissions, for the purpose of reducing carbon footprint by sponsoring environmental projects that reduce greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere, thereby balancing the amount of carbon emissions produced. One carbon offset credit equals one tonne of CO2 or one tonne of other greenhouse gases eliminated from the atmosphere. Carbon offset credits may be obtained from businesses and tree-planting programs, projects that collect and store CO2, or farmers attempting to minimize or recover methane emissions from livestock activities.
So what is the difference between carbon credit and carbon offset? According to some information, although these terms are similar in referring to reducing greenhouse gases in general, carbon offset aims to remove greenhouse gases from the atmosphere, while carbon credits aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions into the atmosphere. For more information on what carbon credits are and the carbon market around the world, please read the article at: https://vuphong.com/carbon-credit-market/
Vu Phong Energy Group









